

"On a New Law Connecting the Periods of Molecular Vibrations".
Light and Matter: Electromagnetism, Optics, Spectroscopy and Lasers.
#Atomic emission spectrum series
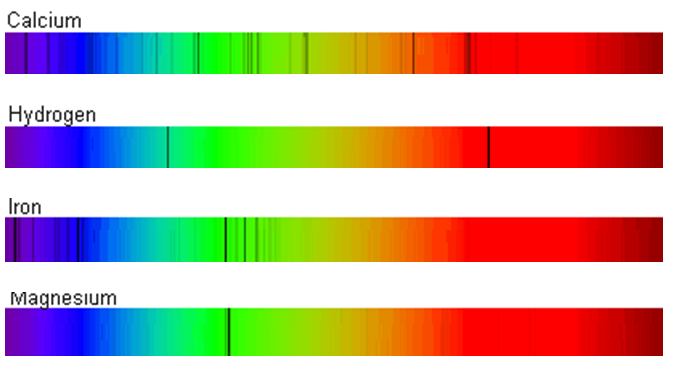
"The New Series in the Spectrum of Hydrogen". "Some Recent Discoveries in Spectrum Series". Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. Others followed this use in the 1930s and the terminology has remained to this day. įriedrich Hund introduced the s, p, d, f notation for subshells in atoms. Heinrich Kayser, Carl Runge and Johannes Rydberg found mathematical relations between the wave numbers of emission lines of the alkali metals. Īrno Bergmann found a fourth series in infrared in 1907, and this became known as Bergmann Series or fundamental series. Rydberg continued the use of sharp and diffuse for the other lines, whereas Kayser and Runge preferred to use the term first subordinate series for the diffuse series. In 1890 the lines that also appeared in the absorption spectrum were termed the principal series. They classified alkali metal spectral lines into sharp and diffuse categories. They were the first to use the term "diffuse" for the lines. They noticed that lines for sodium were alternating sharp and diffuse. Barium īarium has a diffuse series running from infrared to ultraviolet with wavelengths at 25515.7, 23255.3, 22313.4 5818.91, 5800.30, 5777.70 4493.66, 4489.00 4087.31, 4084.87 3898.58, 3894.34 3789.72, 3788.18 3721.17, and 3720.85 Å History Īt Cambridge University George Liveing and James Dewar set out to systematically measure spectra of elements from groups I, II and III in visible light and longer wave ultraviolet that would transmit through air. With strontium vapour, the most prominent lines are from the diffuse series. Calcium Ĭalcium has a diffuse series of triplets and a sharp series of singlets. Magnesium has a diffuse series of triplets and a sharp series of singlets.

This has a diffuse series as well with wavelengths at 6678, 49 Å. Helium when ionised is termed He II and has a spectrum very similar to hydrogen but shifted to shorter wavelengths. Helium has a diffuse series of doublet lines with wavelengths 5876, 44 Å. Helium is in the same category as alkaline earths with respect to spectroscopy, as it has two electrons in the S subshell as do the other alkaline earths. The diffuse series of singlet lines has series letter S and formula 1P-mS. Potassium potassium diffuse series Ī diffuse series of triplet lines is designated by series letter d and formula 1p-md. When n tends to infinity the diffuse and sharp series end up with the same limit. In alkali metals the P terms are split 2 P 3 2 The limit for the series corresponds to electron emission, where the electron has so much energy it escapes the atom.

The Rydberg correction is largest for the S term as the electron penetrates the inner core of electrons more. Since the Electron in the D subshell state is not the lowest energy level for the alkali atom (the S is) the diffuse series will not show up as absorption in a cool gas, however it shows up as emission lines. The terms can have different designations, mD for single line systems, mδ for doublets and md for triplets. One terminology to identify the lines is: 1P-mD But note that 1P just means the lowest P state in the valence shell of an atom and that the modern designation would start at 2P, and is larger for higher atomic numbered atoms. The series is caused by transitions from the lowest P state to higher energy D orbitals. The diffuse series is due to the 3p-nd transitions shown here in blue. \) for a summary).Grotrian diagram for sodium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
